Di Primio Cristina
- Dettagli
- Visite: 2032
 Research scientist
Research scientist
Via Giuseppe Moruzzi, 1
56124 - Pisa
050-3153142
Questo indirizzo email è protetto dagli spambots. È necessario abilitare JavaScript per vederlo.
Research overview
The primary aim of our lab is to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration. Our experimental approach encompasses a range of molecular and cellular techniques, including transcriptomics and interactomics, applied to neuronal cellular models and iPSC-derived neurons. Additionally, we develop biosensors to monitor protein conformational changes and aggregation, and we exploit synthetic virology approaches to engineer viral particles for studying neuronal functions.
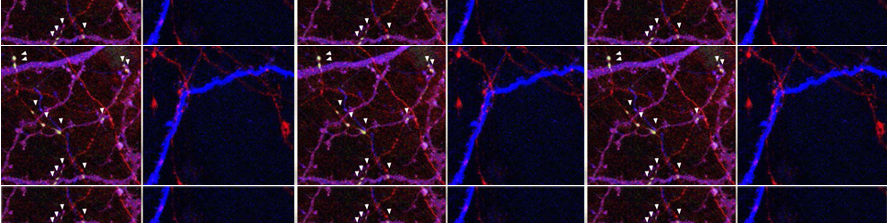
We have described a novel function of the Tau protein involved in Alzheimer's disease. Specifically, we found that in the early stages of the pathology, Tau accumulates in the nuclear compartment and modulates the expression of disease-related genes by reshaping the transcriptional landscape. Additionally, we have described the involvement of Tau misfolding in long-term neuronal damage following SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Furthermore, we developed a FRET-based biosensor that is applied in both in vitro and in vivo aggregation assays to monitor Tau conformational changes at the onset and progression of the pathology. This innovative assay is a powerful tool for screening potential therapeutic compounds against protein aggregation, paving the way for new treatments
Current research projects
 Identification of Nuclear Cofactors of Tau Protein
Identification of Nuclear Cofactors of Tau Protein
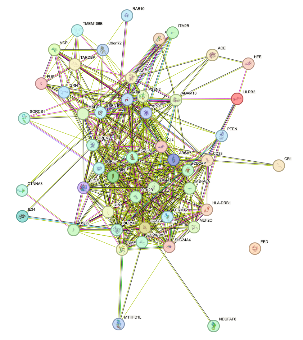
We aim to identify and characterize nuclear cofactors of the Tau protein. Using interactomic experiments, we have identified a list of cofactors, which will be validated and furtheranalyzed using molecular and imaging techniques in hiPSC-derived cortical neurons. The goal is to unravel the interplay between Tau and these cofactors in the early stages of neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease
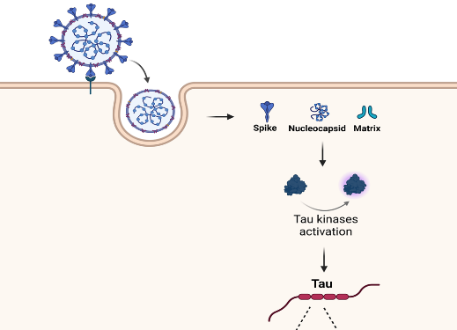 Long-Term Impact of Viral Infections in the CNS
Long-Term Impact of Viral Infections in the CNS
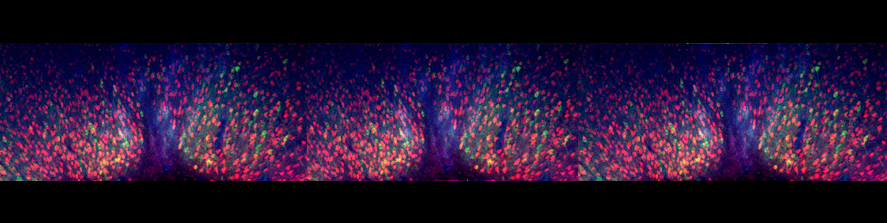
We study the impact of neurotropic viruses on neuronal health by monitoring the misfolding, solubility, and phosphorylation of Tau in neurons infected by current SARS-CoV-2 variants of interest. We have described how viral proteins directly interact with Tau, leading to its misfolding. As part of the "Rete Italiana per la sorveglianza virologica, il monitoraggio immunologico, la formazione e la ricerca in preparazione alla gestione delle Emergenze Infettive (R.I.Pr.E.I.)", we are exploring the link between infection and biomarkers of neurodegeneration, as well as the long-term effects of infection on neuronal health using molecular and imaging techniques.
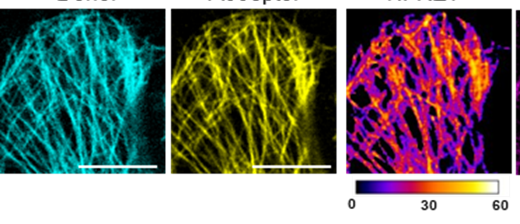 Alzheimer's Disease Biosensor
Alzheimer's Disease Biosensor
We have developed an in vitro platform for anti-aggregation drug screening using our FRET-based biosensor. This tool is employed to screen potential therapeutic candidates. We are also optimizing this tool to create a prototype for diagnostic purposes. The optimization process includes enhancing the biosensor's sensitivity and specificity by refining the fluorescent proteins used and improving assay conditions. We are integrating advanced imaging techniques to better visualize and quantify Tau conformational changes and optimizing a bioactive support for a diagnostic prototype. This innovative assay is a powerful tool for screening potential therapeutic compounds against protein aggregation, paving the way for new treatments
 Synthetic virology: Capturing the Synaptic miRNome
Synthetic virology: Capturing the Synaptic miRNome
Using synthetic virology approaches, we have engineered synthetic virus-like particles with novel functions. Our aim is to collect miRNAs from specific cellular compartments in live neurons. We are creating subcellular miRNome libraries from both healthy and diseased neurons to identify pathological miRNAs. hiPSC-derived cortical neurons will be used for molecular and imaging experiments, as well as for transcriptomics, to identify novel biomarkers.

Meet My Team

Dr. Giacomo Siano, Ph.D.
Senior Post-Doc
His work has been awarded by Airalzh and focuses on the identification of factors involved in protein synthesis alteration during Alzheimer’s disease.
Questo indirizzo email è protetto dagli spambots. È necessario abilitare JavaScript per vederlo.
ORCID: 0000-0003-4320-563

Arianna Scarlatti
PhD student in Neuroscience at Scuola Normale Superiore, working on Tau cofactors involved in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
Questo indirizzo email è protetto dagli spambots. È necessario abilitare JavaScript per vederlo.
ORCID:0009-0000-8407-1671
 Vincenzo Iannone
Vincenzo Iannone
Research fellow working on the long-term impact of neurotropic viruses infection on the Central Nervous System
Questo indirizzo email è protetto dagli spambots. È necessario abilitare JavaScript per vederlo.
 Alì Ataman
Alì Ataman
Master Degree student in Neuroscience at University of Pisa
Questo indirizzo email è protetto dagli spambots. È necessario abilitare JavaScript per vederlo.
Representative publications:
Siano G, Varisco M, Terrigno M, Wang C, Scarlatti A, Iannone V, Groth M, Galas MC, Hoozemans JJM, Cellerino A, Cattaneo A, Di Primio C. Tau mediates the reshaping of the transcriptional landscape toward intermediate Alzheimer's disease stages. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 3;12:1459573. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1459573.
Siano G, Madaro G, Caiazza MC, Allouch A, Varisco M, Mignanelli M, Cattaneo A, Di Primio C. Tau-dependent HDAC1 nuclear reduction is associated with altered VGluT1 expression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 17;11:1151223. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1151223.
Di Primio C, Quaranta P, Mignanelli M, Siano G, Bimbati M, Scarlatti A, Piazza CR, Spezia PG, Perrera P, Basolo F, Poma AM, Costa M, Pistello M, Cattaneo A. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection leads to Tau pathological signature in neurons. PNAS Nexus. 2023 Sep 19;2(9):pgad282. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad282.
Siano G, Falcicchia C, Origlia N, Cattaneo A, Di Primio C. Non-Canonical Roles of Tau and Their Contribution to Synaptic Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 20;22(18):10145. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810145.
Siano G, Micaelli M, Scarlatti A, Quercioli V, Di Primio C, Cattaneo A. The Q336H MAPT Mutation Linked to Pick's Disease Leads to Increased Binding of Tau to the Microtubule Network via Altered Conformational and Phosphorylation Effects. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Dec 2;13:569395. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.569395.
Siano G, Varisco M, Caiazza MC, Quercioli V, Mainardi M, Ippolito C, Cattaneo A, Di Primio C. Tau Modulates VGluT1 Expression. J Mol Biol. 2019 Feb 15;431(4):873-884. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.023. Epub 2019 Jan 18.
Siano G, Caiazza MC, Ollà I, Varisco M, Madaro G, Quercioli V, Calvello M, Cattaneo A, Di Primio C. Identification of an ERK Inhibitor as a Therapeutic Drug Against Tau Aggregation in a New Cell-Based Assay. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Aug 21;13:386. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00386.
Di Primio C, Quercioli V, Siano G, Rovere M, Kovacech B, Novak M, Cattaneo A. The Distance between N and C Termini of Tau and of FTDP-17 Mutants Is Modulated by Microtubule Interactions in Living Cells. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Jun 30;10:210. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00210.
A Complete List of Published Work in My Bibliography: di primio cristina - Search Results - PubMed
ORCID: 0000-0003-2140-3696
Scopus Author ID: 8535205400