Verderio Claudia
- Dettagli
- Visite: 19082
 Research director
Research director
c/o Università di Milano - Bicocca
Via Raoul Follereau, 3
20854 Vedano al Lambro (MB)
Questo indirizzo email è protetto dagli spambots. È necessario abilitare JavaScript per vederlo.
Tel. 02 64488386
Cell-to-cell signaling in brain
Research summary
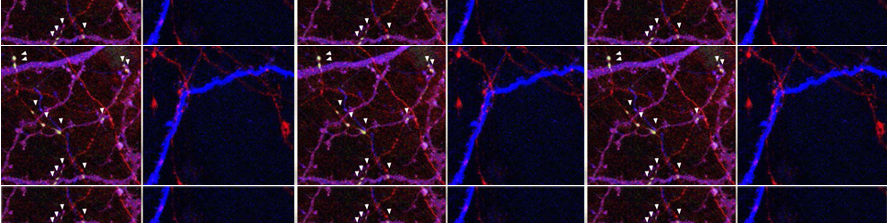
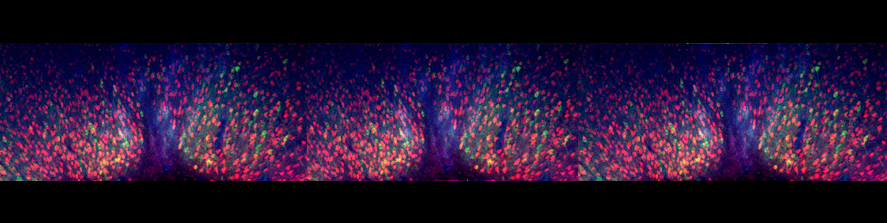
The main goal of the laboratory is to characterize mechanisms of intercellular communication between glial cells and neurons. Recently we focused our attention on an unconventional secretory mechanism which is based on release of extracellular membrane microvesicles (EMVs) into the pericellular space. Through this process, microglial cells heavily influence brain cell functions, either propagating inflammation and causing damage to neurons or playing a supportive, neuroprotective role.
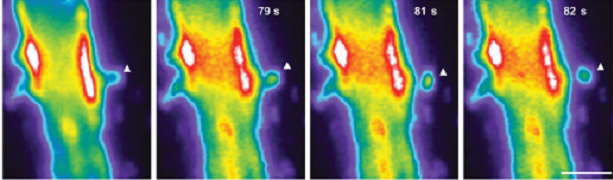
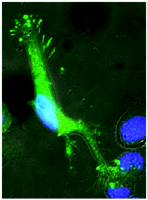
In vivo, microglia produce EMVs which reach the cerebrospinal fluid, where they are emerging as biomarkers of neuroinflammatory diseases. Indeed EMV production reflects the extent of microglial activation, and quantification of EMVs provides useful clinical information to capture disease activity in patients with neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative brain disorders (Verderio et al., 2012; Joshi et al., 2014).
Staff
Ilaria Prada, post-doc
Loredana Riganti, post-doc
Martina Gabrielli, post-doc
Marta Lombardi, PhD student
Giulia D’Arrigo, PhD student
Representative publications
Riganti L, Antonucci F, Gabrielli M, Prada I, Giussani P, Viani P, Valtorta F, Menna E, Matteoli M and Verderio C (2016), Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P) Impacts Presynaptic Functions by Regulating Synapsin I Localization in the Presynaptic Compartment. J Neurosci 3 (16):4624.
Gabrielli M, Battista N, Riganti L, et al. Maccarrone M, Verderio C (2015), Active endocannabinoids are secreted on extracellular membrane vesicles. EMBO Rep. 16(2):213-20.
Joshi P, Turola E., Ruiz A, Bergami A, Dalla Libera D, Benussi L, Giussani P, Magnani G, Comi G, Legname G, Ghidoni R, Furlan R, Matteoli M and Verderio C (2014) Microglia convert aggregated amyloid-β into neurotoxic forms through the shedding of microvesicles. Cell Death & Differentiation, 21:582-93.
Antonucci F, Turola E, Riganti L, Caleo M, Gabrielli M, Perrotta C, Novellino L, Clementi E, Giussani P, Viani P, Matteoli M, Verderio C. (2012), Microglial microvesicles can stimulate neuronal exocytosis via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism. EMBO J. 31(5):1231-40.
C Verderio, L Muzio, E Turola, A Bergami, L Novellino, F Ruffini,L Riganti, I Corradini, M Francolini, L Garzetti, C Maiorino, F Servida, A Vercelli, M Rocca, D Dalla Libera, V Martinelli, G Comi, G Martino, M Matteoli, R Furlan (2012), Myeloid Microvesicles Are a Marker and Therapeutic Target for Neuroinflammation. Ann Neurol., 72:610-14.